- Key Concepts
- Understanding the Fundamentals of the mim OE Runtime
Understanding the Fundamentals of the mim OE Runtime
Purpose
The purpose of the document is to describe the nature and operation of the minOE Runtime.
Intended Readers
The intended readers of this document are software developers, system engineers, application architects, deployment personnel and other technical professionals who want to understand the details of working with mim OE Runtime.
What You Will Learn from this Document
After reading this document you will:
- Understand how the mim OE Runtime turns an independent computing device such as a cell phone into a server on the hybrid edgeCloud
- Understand how to register an edge computing device such as a cell phone with the hybrid edgeCloud using the mim OE Runtime
- Understand how to use the mim OE runtime to deploy and run a microservice on a hybrid edgeCloud
- Have a working knowledge of the runtime resources and services that the mim OE Runtime makes available to microservice automatically
What You Need to Know Before You Start
In order to get the full benefit from reading this document, you need to have:
- A general understanding of edge computing and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- A general understanding of the nature of microservices
Understanding the mim OE Runtime
The mim OE Runtime is a binary file that can be installed on a variety of computing devices such as a desktop computer, laptop computer or Internet of Things device (IoT). for example, an embedded system or a cable television set-top box. Also, you can install the mim OE Runtime on a mobile device such as a cell phone or mobile tablet.
The mim OE Runtime will run on any device that has an operating system that the runtime supports. The following list describes the operating systems supported by the mim OE Runtime
- Android
- iOS
- Windows
- macOS
- Raspian
- Linux Ubuntu
- Beaglebone
- QNX
The mim OE Runtime serves as an intermediary between the host operating system and the code running a edge microservice. (See Figure 1, below.)
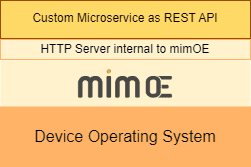
|
|---|
| Figure 1: mim OE interacts with the host operating system to provide a serverless environment upon which to run a custom microservice |
When a computing device has the mim OE Runtime installed that computing device is deemed to be a node within an edge Service Mesh cluster.
The Benefits of the mim OE Runtime
The benefits of using the mim OE Runtime are as follows.
- As mentioned above once the mim OE Runtime is up and running on a computing device, that device is part of a mim OE Cluster within an edge Service Mesh cluster.
- The mim OE Runtime provides all the capabilities required to run a RESTful microservice. By default, the mim OE Runtime installs an HTTP web server automatically. All microservice endpoints running on the node have access to the HTTP web server as a shared resource.
- Once a microservice is deployed on a device running the mim OE Runtime, that microservice has access to other nodes running within a given mim OE Cluster. Access to the nodes is facilitated using the edge Service Mesh in conjunction with the mim OE API to do service discovery and then once identified, microservices in the other nodes can be called to accomplish specific tasks.
Creating mim OE Nodes Using the mim OE Runtime
As mentioned above, creating a mim OE node requires installing the mim OE Runtime on a specific device. The particular steps for installing the mim OE Runtime on a computing device are described in the tutorial, Installing mim OE and the mimik-edge-cli tool on a Linux System or MacOS found in the Tutorials section of this Developer Portal documentation.
Registering a mim OE Node to a user account
Registering a mim OE node to devices running the mim OE Runtime is done automatically when installing the mim OE Runtime on a particular computing device.
However, additional steps are required in order to associate a node running the mim OE Runtime with a particular mimik/mim OE user account. This association is done using the mimik Command Line Tool to create an Access Token from within a node running the mim OE Runtime. An Access Token binds the mim OE node to a particular user account.
The conceptual details about an Access Token are covered in the Key Concept document, Understanding Runtime Tokens. The instructions for using the mimik Command Line Tool to create an Access Token that binds a mim OE node to a user account and thus grants access to the mim OE API and other mim OE nodes are described in the tutorial, QuickStart .
Deploying and running a microservice on an edge computing device
As mentioned previously, once the mim OE Runtime is up and running on an edge computing device, developers can deploy an edge microservice on the particular device. Deploying a microservice on a device running the mim OE Runtime requires understanding mim OE Images and mim OE Containers.
The details of mim OE Images and mim OE Containers are covered in the Key Concepts document, Understanding mim OE Images and mim OE Containers.
In short, developers wanting to make a microservice that runs on the mim OE Runtime will create a custom Node.js project that has the code for the logic of the particular microservice. This custom Node.JS is called an mim OE Image.
You can think of the mim OE Image defined in the Node.js project as a template from which the mim OE container is created. Developers use the mimik Command Line Tool to execute the command set mimik-edge-cli image deploy to create the .tar file that represents the particular mim OE container.
The container's .tar file has a microservice of interest. You'll use the mimik Command Line Tool to execute the command set mimik-edge-cli container deploy to deploy and run the container's microservice on the given mim OE node.
Understanding the runtime computing resources and services provided by the mim OE Runtime
The thing to keep in mind with regard to the mim OE Runtime is that, as mentioned previously, everything you need to run your microservice is provided by the runtime. The microservice's logic is programmed in a custom Node.JS project.
The mim OE Runtime provides the HTTP web server upon which your RESTful microservice will run. Also, the mim OE Runtime provides access to the edge Service Mesh, which in turn allows your code to discover and use other microservices running on different nodes in the.
In effect, the mim OE Runtime provides a serverless computing environment for running microservices.